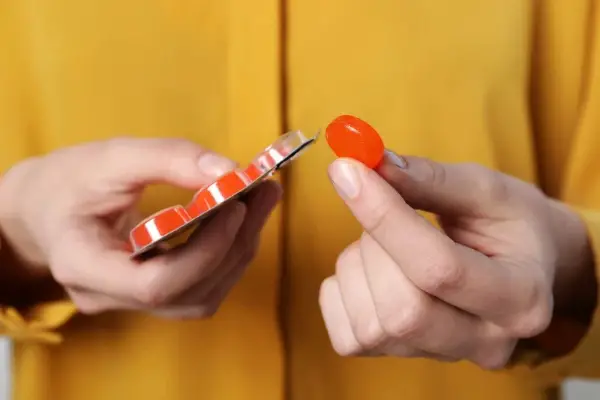
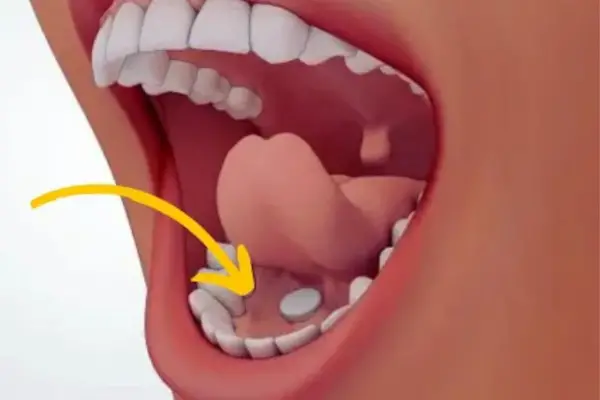
Sublingual B12 tablets are not toxic when swallowed but this is not in accordance with the intended usage. SL tablets are specifically optimized for absorption through the mucosa of the buccal cavity and become less effective if swallowed in some cases. This is so because sublingual B12 administration is independent of the level of free intrinsic factor unlike oral.
Besides, oral B12 tablets are often formulated with intrinsic factors to enable absorption but the same can’t be said for sublingual B12.
As a result, swallowing sublingual B12 may result in less effect in individuals with pernicious anemia, Crohn’s disease, gastritis, or the elderly who use many medications that can interfere with the absorption of vitamin B12.
Vitamin B12 can also be absorbed by passive diffusion in the stomach and intestines but only 1% of the stated nutrient dose is absorbed. So, a higher dose will be required.
Why Do You Have To Hold Sublingual Vitamin B12 Under Your Tongue?
The sublingual method of administration is recommended to enhance its bioavailability, which is essentially the rate and extent to which the vitamin is absorbed and becomes available at the site of physiological activity.
With this method of administration, there is greater absorption directly into the bloodstream through the mucous membranes found under the tongue. Besides, the absorption of vitamin B12 in oral administration is significantly reliant on the presence of an intrinsic factor, a protein secreted by the stomach that is necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12 in the small intestine.
In conditions like pernicious anemia, where intrinsic factor is deficient due to attack of the gastric parietal cells by autoantibodies, the effectiveness of oral supplementation can be markedly reduced, making sublingual administration or intramuscular injections more effective alternatives.
According to the study, the effectiveness of both oral and sublingual B12 administration was the same. A similar study performed by the British Pharmacological Society showed that after 8 weeks of vitamin B12 administration in 30 subjects, the serum vitamin B12 level was slightly higher for the sublingual route than oral.
Furthermore, the sublingual route offers the added benefit of bypassing the first-pass metabolism in the liver, a process where the concentration of a drug is greatly reduced before it reaches systemic circulation. This first-pass effect can limit the effectiveness of many drugs and supplements when taken orally, as a significant portion of the substance is metabolized in the liver and intestines before it can exert its effects on the body.
By avoiding this pre-systemic extraction, sublingual administration ensures a higher proportion of vitamin B12 is available for use by the body, potentially enhancing its overall efficacy. This method is particularly useful for individuals who require vitamin B12 supplementation but have conditions that affect the digestive system’s ability to process and absorb nutrients effectively.
Conditions That Can Disrupt Intrinsic Factor Production
Conditions that affect the production of intrinsic factors, essential for vitamin B12 absorption, include:
- Pernicious Anemia: An autoimmune condition attacking stomach cells that produce intrinsic factors.
- Atrophic Gastritis: Inflammation and thinning of the stomach lining, reducing intrinsic factor production.
- Gastrectomy: Surgical removal of part or all of the stomach.
- H. pylori Infection: Can lead to atrophic gastritis, affecting intrinsic factors.
- Certain Medications: Like Proton pump inhibitors and antibiotics, affect stomach acid and intrinsic factors.
- Congenital Intrinsic Factor Deficiency: A rare inherited condition with no intrinsic factor production.
- Crohn’s Disease: Affects vitamin B12 absorption, indirectly impacting intrinsic factor’s role.
How To Correctly Take Sublingual B12
Taking sublingual vitamin B12 correctly can enhance its absorption and efficacy. Sublingual B12 is designed to be absorbed directly into your bloodstream through the mucous membranes under your tongue, bypassing the digestive tract. Here’s how to correctly take sublingual B12:
- Check the Dosage: Before taking, ensure you know the recommended dosage as per your healthcare provider’s instructions or the product label.
- Clean Your Mouth: For optimal absorption, it’s a good idea to take the supplement after brushing your teeth in the morning or ensure your mouth is clean.
- Place Under the Tongue: Place the B12 tablet or drop it under your tongue. Avoid touching the tablet with your hands too much to prevent it from dissolving prematurely.
- Allow It to Dissolve: Let the tablet or liquid dissolve completely under your tongue. Do not swallow it whole or chew it. The absorption begins as it dissolves.
- Wait Before Swallowing: Once the tablet has fully dissolved, try to wait a few moments before swallowing any remaining liquid. This gives the mucous membranes more time to absorb the vitamin.
- Avoid Eating or Drinking Immediately: Wait a few minutes after taking sublingual B12 before eating or drinking. This ensures that the vitamin is fully absorbed and doesn’t get washed away.
- Consistent Use: For best results, take your sublingual B12 at the same time each day. Consistency helps maintain steady vitamin levels in your body.
- Follow Medical Advice: Always follow the guidance of your healthcare provider regarding the use of sublingual B12, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Sources:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30632091/
https://journals.innovareacademics.in/index.php/ijpps/article/download/5513/pdf_1243
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0261561418300712